odbc and php mssql support for cloudlinux
For your Cloudlinux or a different Redhat based server, add the appropriate version repo below to your server.
#RHEL 7 and Oracle Linux 7
#curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/7/prod.repo | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/mssql-release.repo
#RHEL 8 and Oracle Linux 8
# curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/8/prod.repo | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/mssql-release.repo
#RHEL9
# curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/9/prod.repo | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/mssql-release.repo
Delete any potentially conflicting packages from the system.
# yum remove unixODBC-utf16 unixODBC-utf16-devel
Install odbc package from Microsoft repo
ACCEPT_EULA=Y yum install -y msodbcsql17 unixODBC-devel
Go to the PHP selector settings of the hosting where you will connect to Microsoft SQL Server with your PHP codes and activate the pdo, pdo_odbc, pdo_sqlsrv, sqlsrv plugins and optionally the pdo_dblib plugin.
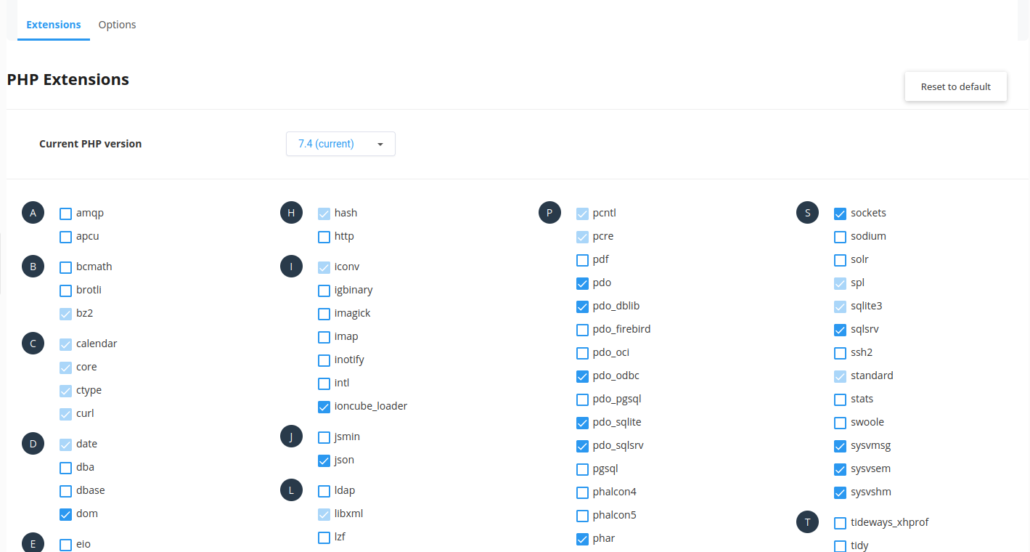
You need to include the package you installed for Cloudlinux OS in the cagefs structure. This will not be necessary on other RH-based systems…
# cagefsctl –addrpm unixODBC
# cagefsctl –force-update
Then test your connection with a test script.
Sample Code
<?php
$server = "";
$database = "";
$kullaniciadi = "";
$sifre = "";
$Karakter = "utf-8";
$Port = "1433";
try
{
$db = new PDO("sqlsrv:Server=$server;Database=$database;", "$kullaniciadi", "$sifre");
//$db = odbc_connect("Driver={SQL Server};Server=$server,$Port;Database=$database;", $kullaniciadi, $sifre);
if ($db)
echo "success";
}
catch (Exception $e)
{
//Eğer bağlantı sırasında bir hata oluşursa ekrana oluşan hata bastırılacaktır.
echo $e->getMessage();
}
exit;
?>


 Linux Support Here
Linux Support Here